Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (40): 6553-6561.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.40.027
Meta-analysis on endobutton plate versus the other fixation methods for acromioclavicular joint dislocation
Wang Zhi-zhou, Qu Guang-hua, Han Ya-jun, Xu Chao, Yilihamu·Tuoheti
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2014-08-13Online:2014-09-24Published:2014-09-24 -
Contact:Yilihamu? Tuoheti, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Zhi-zhou, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Scientific Innovation Fund by Xinjiang Medical University in 2012, No. XJC201253
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhi-zhou, Qu Guang-hua, Han Ya-jun, Xu Chao, Yilihamu•Tuoheti. Meta-analysis on endobutton plate versus the other fixation methods for acromioclavicular joint dislocation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(40): 6553-6561.
share this article
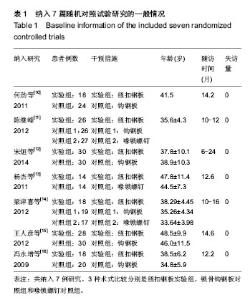
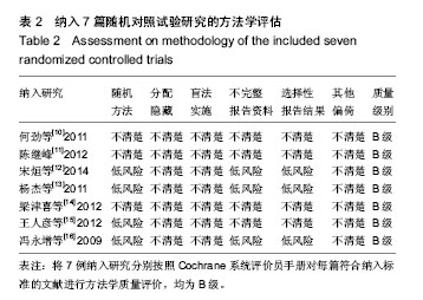
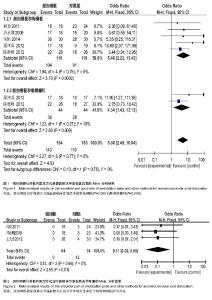
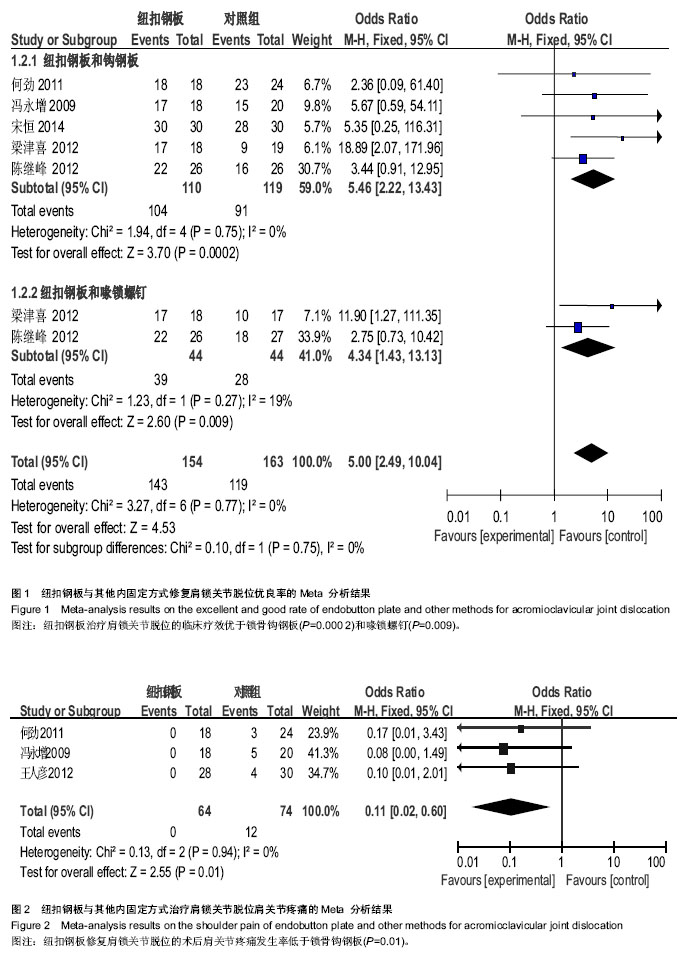
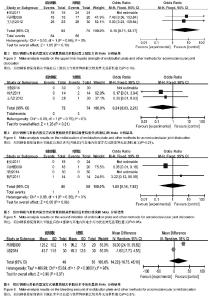
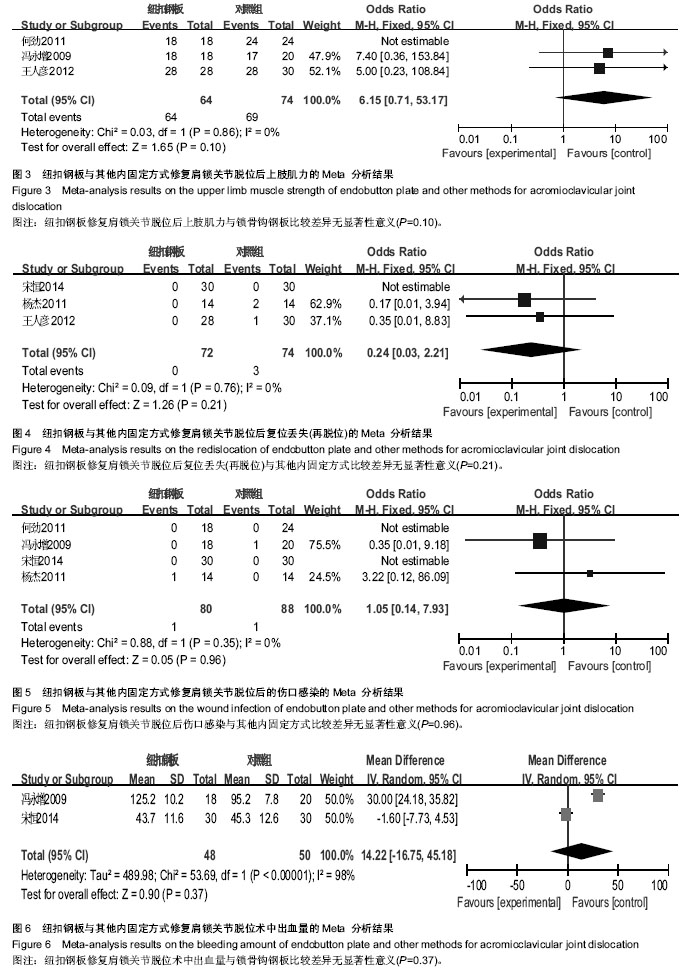
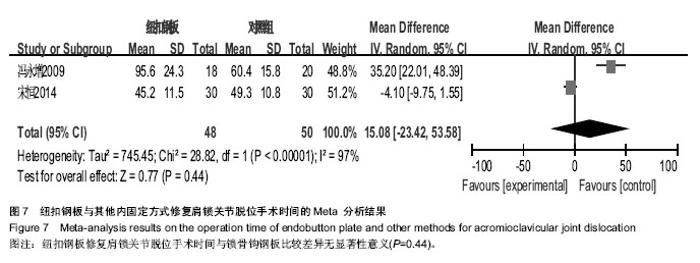
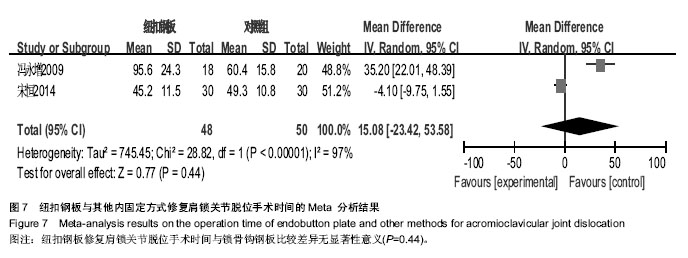
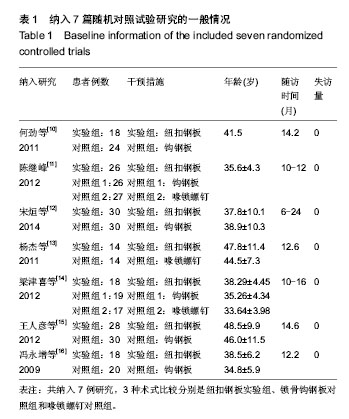
2.1 文献检索结果 输入检索词后初检到相关文献264篇,经仔细阅读文题及摘要后,并排除重复发表的研究以及回顾性研究,从而得到肩锁关节脱位纽扣钢板内固定治疗随机研究的文献46篇,最后通过全文阅读,电话询问作者及仔细阅读原文并提取资料,排除39篇不符合纳入标准的文献,最终纳入7篇文献。 2.2 纳入研究的设计 纳入的7个研究均为随机对照试验,研究地点均在中国[10-16]。 2.3 纳入研究对象及一般情况 7个研究共纳入359例患者,其中纽扣钢板实验组152例,锁骨钩钢板对照组共149例,喙锁螺钉对照组共58例。其中只有2个研究是3种不同方式比较,余均为2种治疗方式相比较。各纳入研究的基本情况见表1。 2.4 纳入研究的方法学评估 由2名评价者独立根据预定的纳入和排除标准筛选文献、进行质量评价和资料提取,如存在分歧则通过协商或征求第3方意见解决。按照Cochrane系统评价员手册对每篇符合纳人和排除标准的文献进行方法学质量评价(表2)。 2.5 优良率Meta分析结果 纽扣钢板与锁骨钩钢板:5个随机对照试验报道了这2种方式治疗效果的优良率(karlsson评定标准)[10-12,14,16],纽扣钢板组110例,锁骨钩钢板组119例,异质性分析显示,各研究无明显异质性[Chi2=1.94,df=4(P=0.75),I2=0%],采用固定效应模型进行分析,OR=5.46,95%CI(2.22,13.43),P=0.000 2,结果显示2种内固定方式优良率差异有显著性意义(图1)。 纽扣钢板和喙锁螺钉:2个随机对照试验报道了这两种方式治疗效果的优良率(karlsson评定标准)[11,14],纽扣钢板组44例, 喙锁螺钉组44例,异质性分析显示,各研究无明显异质性[Chi2=1.23,df=1(P=0.27),I2=19%],采用固定效应模型进行分析,OR=4.34,95%CI(1.43,13.13),P=0.009,结果显示2种内固定方式优良率差异有显著性意义(图1)。 2.6 肩关节疼痛Meta分析结果 3个随机对照试验报道了肩关节疼痛发生情况[10,15-16],共138例,其中纽扣钢板组64例,锁骨钩钢板组74例,异质性分析显示,各研究无明显异质性[Chi2=0.13,df=2(P=0.95),I2=0%],故采用固定效应模型进行分析,OR=0.11,95%CI(0.02,0.60),P=0.01,结果显示纽扣钢板修复肩锁关节脱位后肩关节疼痛与其他内固定方式比较差异有显著性意义(图2)。 2.7 治疗后上肢肌力Meta分析结果 3个随机对照试验报道固定后上肢肌力情况[10,15-16],共138例。其中纽扣钢板组64例,锁骨钩钢板组74例,以肌力为5级或4级的患者疗效评定为优良,以肌力≤3的患者疗效评定为差进行统计学分析。异质性分析显示,各研究无明显异质性[Chi2= 0.03,df=1(P=0.86),I2=0%],故采用固定效应模型进行分析,OR=6.15,95%CI(0.71,53.17),P=0.10,结果显示纽扣钢板治疗肩锁关节脱位后上肢肌力与其他内固定方式比较差异无显著性意义(图3)。 2.8 复位丢失(再脱位)Meta分析结果 3个随机对照试验报道手术后复位丢失(再脱位)情况[12-13,15],共146例。其中纽扣钢板组72例,锁骨钩钢板组60例,喙锁螺钉14例。异质性分析显示,各研究无明显异质性[Chi2=0.09,df=1 (P=0.76),I2=0%],故采用固定效应模型进行分析OR=0.24,95%CI(0.03,2.21),P=0.21,结果显示纽扣钢板修复肩锁关节脱位后复位丢失(再脱位)与其他内固定方式比较差异无显著性意义(图4)。 2.9 术后伤口感染Meta分析结果 4个随机对照试验报道手术后伤口感染情况[10,12-13,16],共168例。其中纽扣钢板组80例,锁骨钩钢板组74例,喙锁螺钉14例。异质性分析显示,各研究无明显异质性[Chi2=0.88,df=1(P=0.35),I2=0%],故采用固定效应模型进行分析,OR=1.05,95%CI(0.14,7.93),P=0.96,结果显示纽扣钢板修复肩锁关节脱位后伤口感染与其他内固定方式比较差异无显著性意义(图5)。 2.10 术中出血量Meta分析结果 2个随机对照试验报道术中出血量情况[12,16],共98例。其中纽扣钢板组48例,锁骨钩钢板组50例。异质性分析显示,各研究有明显异质性[Chi2=53.69,df=1(P < 0.000 01),I2=98%],故采用随机效应模型进行分析,MD=14.22,95%CI(-16.75,45.18),P=0.37,结果显示纽扣钢板修复肩锁关节脱位术中出血量与其他内固定方式比较差异无显著性意义(图6)。 2.11 手术时间Meta分析结果 2个随机对照试验报道手术时间情况[12,16],共98例。其中纽扣钢板组48例,锁骨钩钢板组50例。异质性分析显示,各研究有明显异质性[Chi2=28.82,df=1(P < 0.000 01),I2=97%],故采用随机效应模型进行分析,MD=15.08,95%CI(-23.42,53.58),P=0.44,结果显示纽扣钢板修复肩锁关节脱位手术时间与其他内固定方式比较差异无显著性意义(图7)。"
| [1] Nordqvist A, Petersson CJ. Incidence and causes of shoulder girdle injuries in an urban population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1995;4(2): 107-112.
[2] Chillemi C, Franceschini V, Dei Giudici L, et al. Epidemiology of Isolated Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation. Emerg Med Int. 2013;2013:171609.
[3] Provencher MT, LeClere L, Romeo AA, et al. Avoiding and Managing Complications of Surgery of the Acromioclavicular Joint. Compl Knee Shoulder Surg. 2009: 245-264.
[4] Kim AC, Matcuk G, Patel D, et al. Acromioclavicular joint injuries and reconstructions: a review of expected imaging findings and potential complications. Emerg Radiol. 2012; 19:399-413.
[5] Horst K, Dienstknecht T, Pape HC, et al. Treatment of Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation. Bone and Joint Injuries. Eur Man Med. 2014: 35-43.
[6] Struhl S. Double Endobutton Technique for Repair of Complete Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocations. Tech Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;8(4):175-179.
[7] Wei HF, Chen YF, Zhang CQ, et al.Triple endobuttton technique for the treatment of acute complete acromioclavicular joint dislocations: preliminary results. Int Orthop. 2011;35:555-559.
[8] Li H, Wang C, Wang J, et al. Restoration of horizontal stability in complete acromioclavicular joint separations: surgical technique and preliminary results. Eur J Med Res. 2013; 18:42.
[9] Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327(7414): 557-560.
[10] 何劲,赵银必,周忠华,等.RockwoodIII-IV型肩锁关节脱位两种手术方式的比较研究[J].中国医学创新,2011,8(31):6-8.
[11] 陈继峰. Rockwood III-V型肩锁关节脱位的三种治疗方法比较研究[J].现代诊断与治疗, 2012 ,23(4):336-337.
[12] 宋烜,陈羽,子树明,等. 带袢钢板治疗肩锁关节脱位[J].临床骨科杂志,2014 ,17(1):40-42.
[13] 杨杰,赵友明,孙辽军,等.喙锁螺钉与双Endobutton钢板治疗肩锁关节脱位的临床研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,21(7):598-603.
[14] 梁津喜,潘哲强,杨成伟,等.三种治疗RockwoodⅢ-V型肩锁关节脱位方法的对比研究[J].全科医学临床与教育,2012,10(1): 28-30.
[15] 王人彦,陆建阳,孟春,等.双Endobutton钢板治疗肩锁关节脱位的临床研究[J].浙江医学,2012,34(22):1815-1817.
[16] 冯永增,洪建军,陈鸿亮,等.锁骨钩钢板与双Endobutton钢板治疗肩锁关节脱位的对比研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(11): 1009-1014.
[17] Duindam N. Comparison between open and arthroscopic procedures for lateral clavicle resection. Int Orthop. 2013.
[18] Beaver AB, Parks BG, Hinton RY. Biomechanical analysis of distal clavicle excision with acromioclavicular joint reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(7):1684-1688.
[19] Johansen JA,Grutter PW,McFarland EG, et al. Acromioclavicular joint injuries: indications for treatment and treatment options. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(2 Suppl):70-82.
[20] Kienast B, Thietje R, Queitsch C, et al. Mid-term results after operative treatment of rockwood grade III-V Acromioclavicular joint dislocations with an AC-hook-plate. Eur J Med Res. 2011;16: 52-56.
[21] Di Francesco A, Zoccali C, Colafarina O, et al. The use of hook plate in type III and V acromioclavicular Rockwood dislocations: clinical and radiological midterm results and MRI evaluation in 42 patients. Injury. 2012; 43:147-152.
[22] ElMaraghy AW, Devereaux MW, Ravichandiran K, et al. subacromial morphometric assessment of the clavicle hook plate. Injury. 2010;41(6): 613-619.
[23] Millett PJ, Braun S, Gobezie R, et al. Acromioclavicular joint reconstruction with coracoacromial ligament transfer using the docking technique. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10: 6.
[24] Baldwin K, Namdari S, Andersen JR, et al. Luggage Tag Technique of Anatomic Fixation of Displaced Acromioclavicular Joint Separations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:259-265.
[25] 伊力哈木托合提,曲广华,桂和,等.喙肩韧带转位治疗Ⅲ度肩锁关节脱位的临床疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2011,26(5): 414-416.
[26] Kovilazhikathu Sugathan H, Dodenhoff RM. Management of Type 3 Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: Comparison Long-TermFunctional Results of Two Operative Methods. ISRN Surg. 2012;2012:580504.
[27] Sandmann GH, Martetschläger F, Mey L, et al. Reconstruction of displaced acromio-clavicular joint dislocations using a triple suture-cerclage:description of a safe and efficient surgical technique. Patient Saf Surg. 2012;6:25.
[28] Dewar FP, Barrington TW. The treatment of chronic acromio-clavicular dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965;47: 32-35.
[29] 姜春岩,朱以明,王满宜,等.联合腱外侧半肌腱反转移位重建喙锁韧带治疗肩锁关节脱位[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2005,7(9): 803-807.
[30] Gille J, Heinrichs G, Unger A, et al. Arthroscopic-assisted hook plate fixation for acromioclavicular joint dislocation. Int Orthop. 2013;37:377-382.
[31] Yoo YS, Seo YJ, Noh KC, et al. Arthroscopically assisted anatomical coracoclavicular.ligament reconstruction using tendon graft. Int Orthop. 2011;35(7):1025-1030.
[32] Ranne JO, Sarimo JJ, Rawlins MI, et al. All-arthroscopic double-bundle coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction using autogenous semitendinosus graft: a new technique. Arthrosc Tech. 2012;1(1):e11-e14.
[33] 王海明,陈云丰,陆叶,等. Triple-Endobutton技术与锁骨钩钢板置入治疗肩锁关节脱位的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16 (17):3105-3110.
[34] 邹明,骆宇春,柏广富,等.两种方法治疗RockwoodⅢ型肩锁关节脱位的疗效对比分析[J].重庆医学,2012,41(15): 1486-1488.
[35] 赵立连,张耀南,薛庆韵,等.改良Dewar法和关节镜下双钮扣钢板固定法治疗肩锁关节脱位的对比分析[J].中华医学杂志,2011, 91(23): 1587-1590.
[36] 汪李军,杨惠林,史源欣,等.双Endobutton技术与锁骨钩钢板治疗TossyIII型肩锁关节脱位的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013,15(4):283-287.
[37] 田竞,于海龙,薛海鹏,等. Endobutton技术治疗肩锁关节脱位失效的原因分析[J].中国骨与关节外科,2012,5(6):497-500.
[38] 朱建炜,刘瑶,张建华,等.三重固定纽扣钢板解剖重建陈旧性Ⅲ度肩锁关节脱位[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(2): 201-204. |
| [1] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [2] | Ye Xiang-yang, Sun Xiang, Tang Li-xin, Zhen Ping, Geng Bin, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo. Acetabular liner wear of cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene for total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1143-1148. |
| [3] | Zou Wei, Xiao Jie, Long Hao, Zhang Yang, Wu Chen, Du Yu-hui, Feng Ming-xing, Zhou Chang-jun. Screw placement selection of minimally invasive percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 356-361. |
| [4] | Chen Lu-yao, Hu Shi-qiang, Wang Xiao-ping, Wu Wei-wei, Wei Zhan-tu, Huang Jian. Accuracy of digital orthopedic three-dimensional reconstruction for thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 373-377. |
| [5] | Du Shi-yao, Zhou Feng-jin, Ni Bin, Chen Bo, Chen Jin-shui. Finite-element analysis of a novel posterior atlantoaxial restricted non-fusion fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 383-389. |
| [6] | Liu Jun, Liao Su-ping. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of Kirschner nails and external fixation for Bennett fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 390-395. |
| [7] | Sheng Xiao-lei, Yuan Feng, Li Zhi-duo, Yang Yu-ming, Lu Hai-tao, Zhang Jun-wei. Comparison of the accuracy of lower cervical anterior transpedicular screws between three-dimensional printing assembly navigation template and free hand placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 406-411. |
| [8] | Wu Min-hao, Sun Wen-chao, Yan Fei-fei, Xie Yuan-long, Hou Zhi-qiang, Feng Fan, Cai Lin . Treatment research and new progress of early-onset scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 433-439. |
| [9] | Zhang Tai-liang, Zhang Lei, Lian Zhi-ming, Yang Guang-zhong. Effect of remnant preservation on recovery of knee proprioception in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 471-477. |
| [10] | Wang Lei, Wang Feng-feng, Ma Yan-hui, Zhang Jie, Hu Fang, Ma Gai-ping, Liu Mei-mei, Ma Zhang-wen. Meta analysis of clinical outcome of intramedullary nails versus locking plates for two-part proximal humerus fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 478-484. |
| [11] | Zha Yuan-yu, Yang Yang, Chen Shu-zhen, Wei Ren-xiong, Zhang Shu-wei, Jin Wei. Meta-analysis of posterior laminectomy and instrumented fusion versus laminoplasty in treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 485-492. |
| [12] | Hu Jun, Zhang De-qiang, Tang Xin. Postoperative quality of life of internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2953-2960. |
| [13] | Jiang Wei, Yuan Feng. Unilateral pedicle screw fixation combined with translaminar facet screw fixation versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lower lumbar degenerative diseases: a 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2973-2979. |
| [14] | Wang Xiu-ping, Sun Rui-bo, Liu You-wen, Zhang Ying, Jia Yu-dong, Yang Yu-xia, Wang Hui-chao. Femoral neck fractures fixed with intramedullary cannulated screws: factors for postoperative functional recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2999-3004. |
| [15] | Liu Gang, Zhang Lei, Wang Guo-you, Zhou Xin, Zhang Tao, Guan Tai-yuan, Guo Xiao-guang, Fu Shi-jie. Double-row suture anchors under arthroscopy for avulsion-type greater tuberosity fractures (Mutch type I) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3005-3010. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||